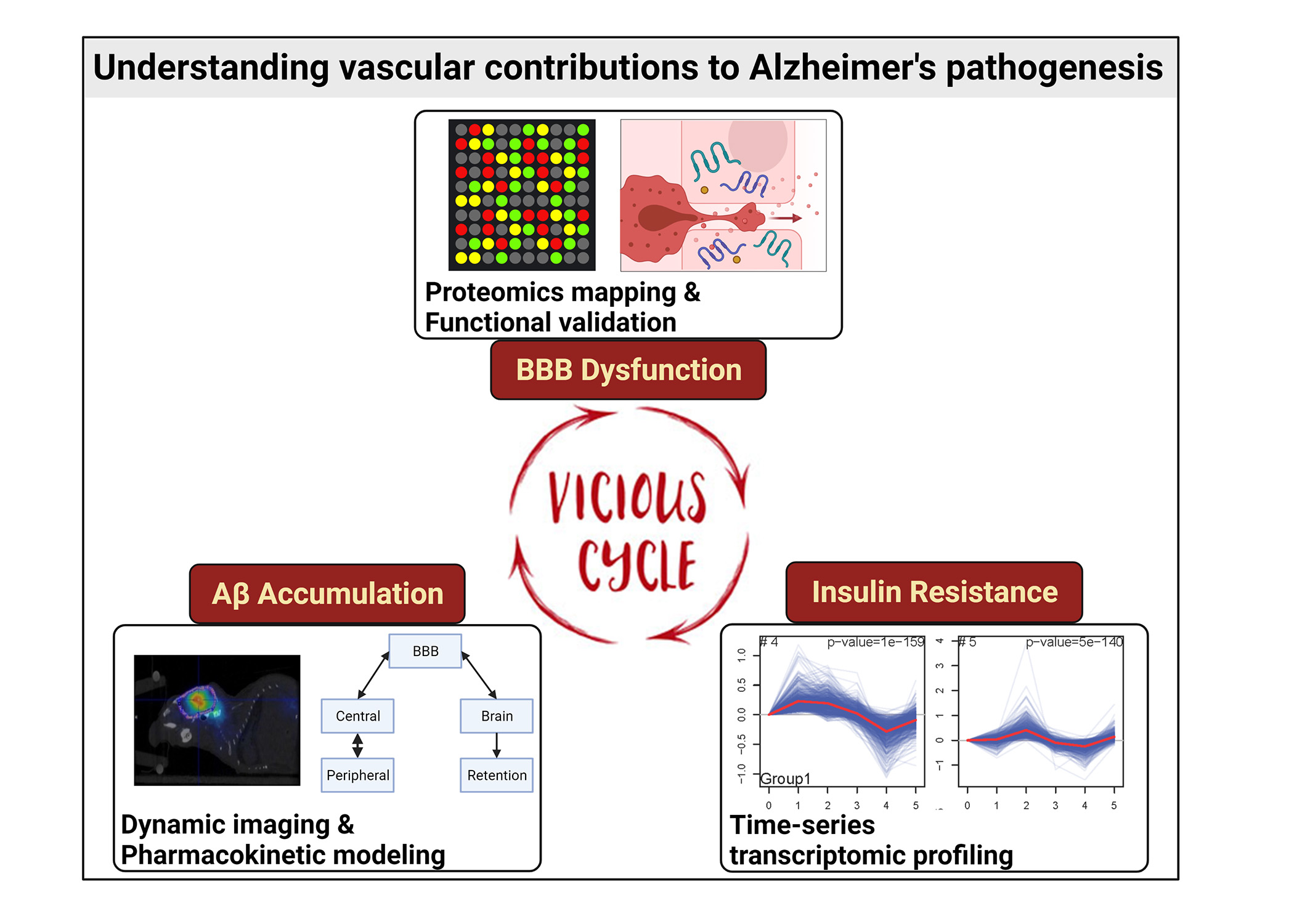
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) plays a critical role in removing toxic amyloid beta (Aβ) peptides from the brain in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Studies have shown that endothelial insulin signaling regulates Aβ trafficking at the BBB but the underlying mechanisms are poorly understood. Further, disrupted trafficking could promote Aβ accumulation within the BBB endothelium which increases endothelial insulin resistance and augments BBB dysfunctions.
PhD student Zengtao Wang (Pharmaceutics), in a project called “Pharmacokinetics of Amyloid-Beta Protein Accumulation in the Blood-Brain Barrier Endothelium and Its Role in Cerebrovascular Dysfunctions in Alzheimer’s Disease,” will characterize molecular mechanisms by which insulin signaling regulates Aβ trafficking at the BBB by mapping the insulin-responsive pathways using time-series multi-omics data. Next, quantitative analysis of Aβ trafficking and accumulation kinetics will be conducted using dynamic imaging and mathematical modeling. Finally, the pathological synergism between insulin resistance and Aβ exposure will be elucidated by proteomics assays and functional validation. The multi-dimensional data thus obtained will be integrated through systems pharmacology approaches to advance the understanding of vascular contribution to AD pathogenesis.
Some funding for this project was provided by a 2022 University of Minnesota Informatics Institute MnDRIVE PhD Graduate Assistantship. The UMII MnDRIVE Graduate Assistantship program supports U of M PhD candidates pursuing research at the intersection of informatics and any of the five MnDRIVE areas:
- Robotics, Sensors and Advanced Manufacturing
- Global Food Ventures
- Advancing Industry, Conserving Our Environment
- Discoveries and Treatments for Brain Conditions
- Cancer Clinical Trials
This project is part of the Discoveries and Treatments for Brain Conditions MnDRIVE area.
Research Computing partners:
- University of Minnesota Informatics Institute
Complete list of 2022 UMII MnDRIVE PhD Graduate Assistantships.